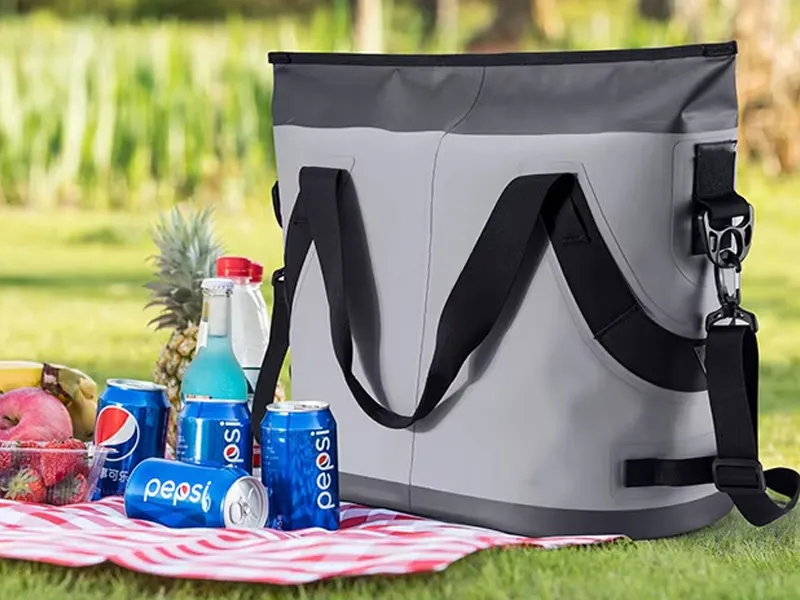
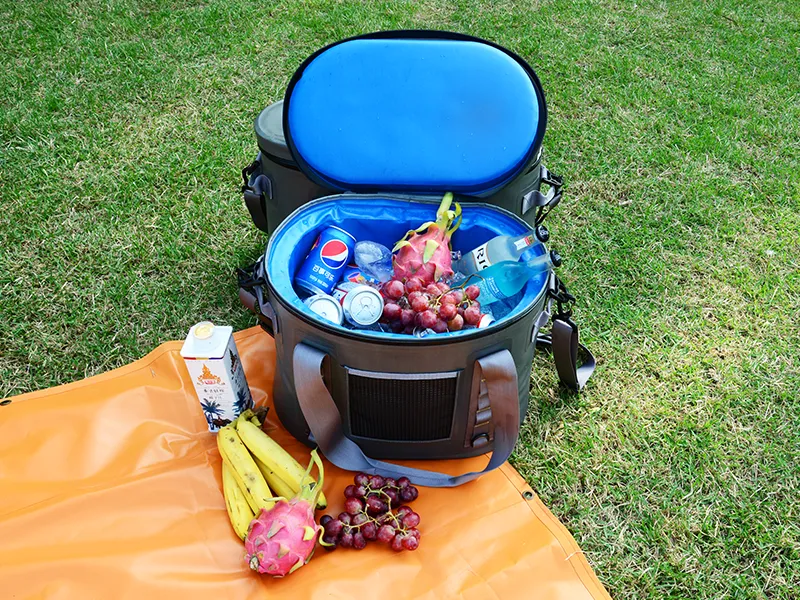
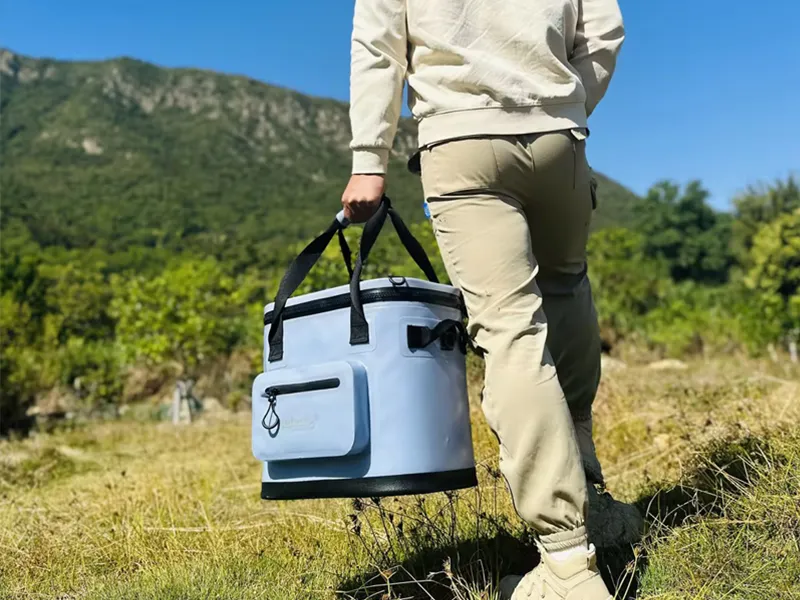
Equipment
Our commitment to Quality: The Sealock Laboratory.
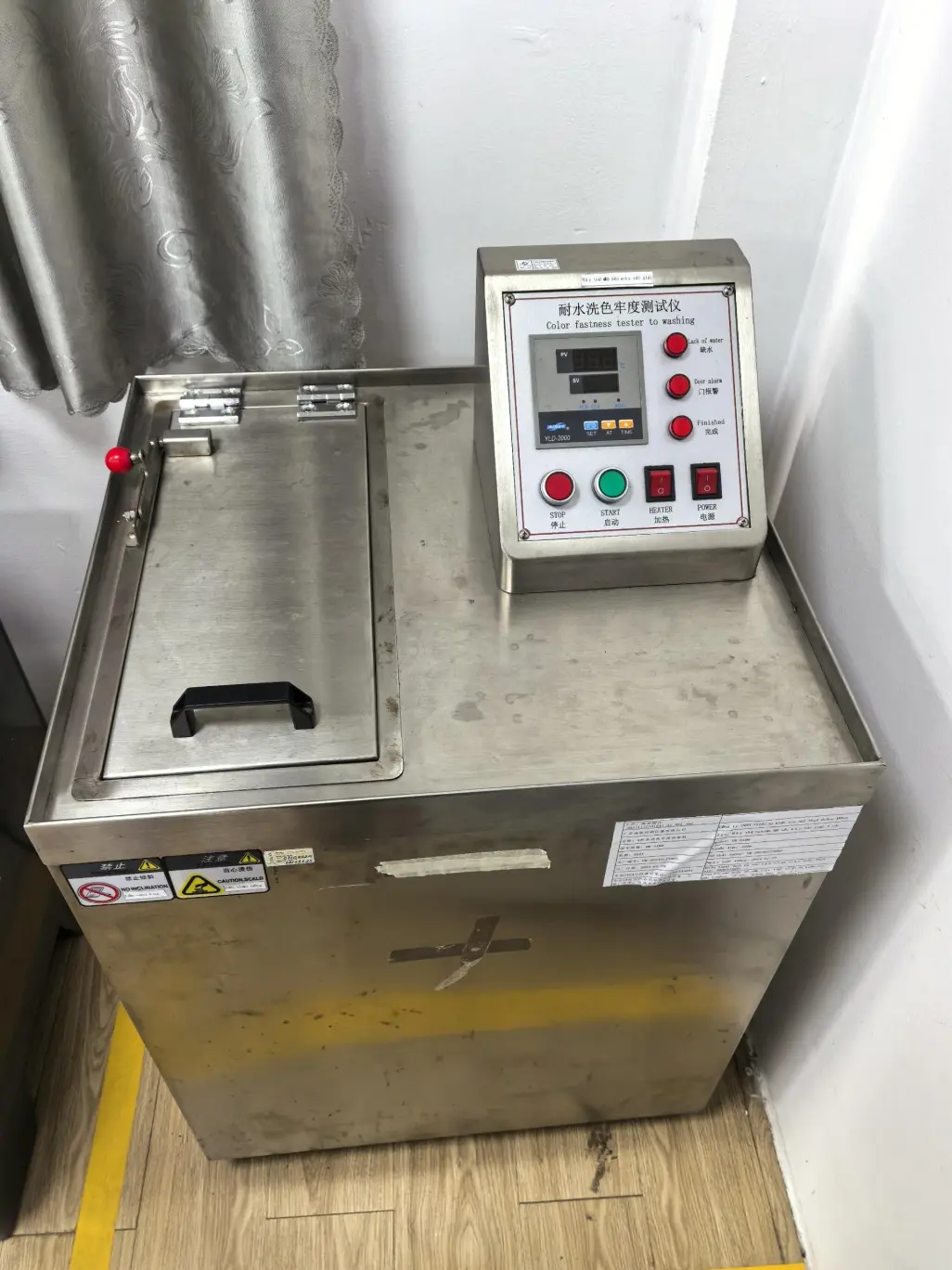
We are equipped with advanced apparatus including high-end testing equipment such as tensile testers, bonding force detectors, zipper fatigue testing machines, salt spray test chambers, and friction color fastness testers.
This data-driven approach enables us to maintain a scientific and stringent quality management system. It ensures a seamless transition from R&D validation to mass production, laying a solid foundation for the durability and reliability of every product we deliver.
|
Production Equipment: |
|
|
Name |
Quantity |
|
Cutting Machine |
17 |
|
High Frequency Plastic Welding Machine |
236 |
|
Post Bed Sewing Machine |
70 |
|
Flat Bed Sewing Machine |
116 |
|
Computerized Sewing Machine |
105 |
|
Edge Coating Machine |
21 |
Test Machine



Salt spray tester testing methods and procedures
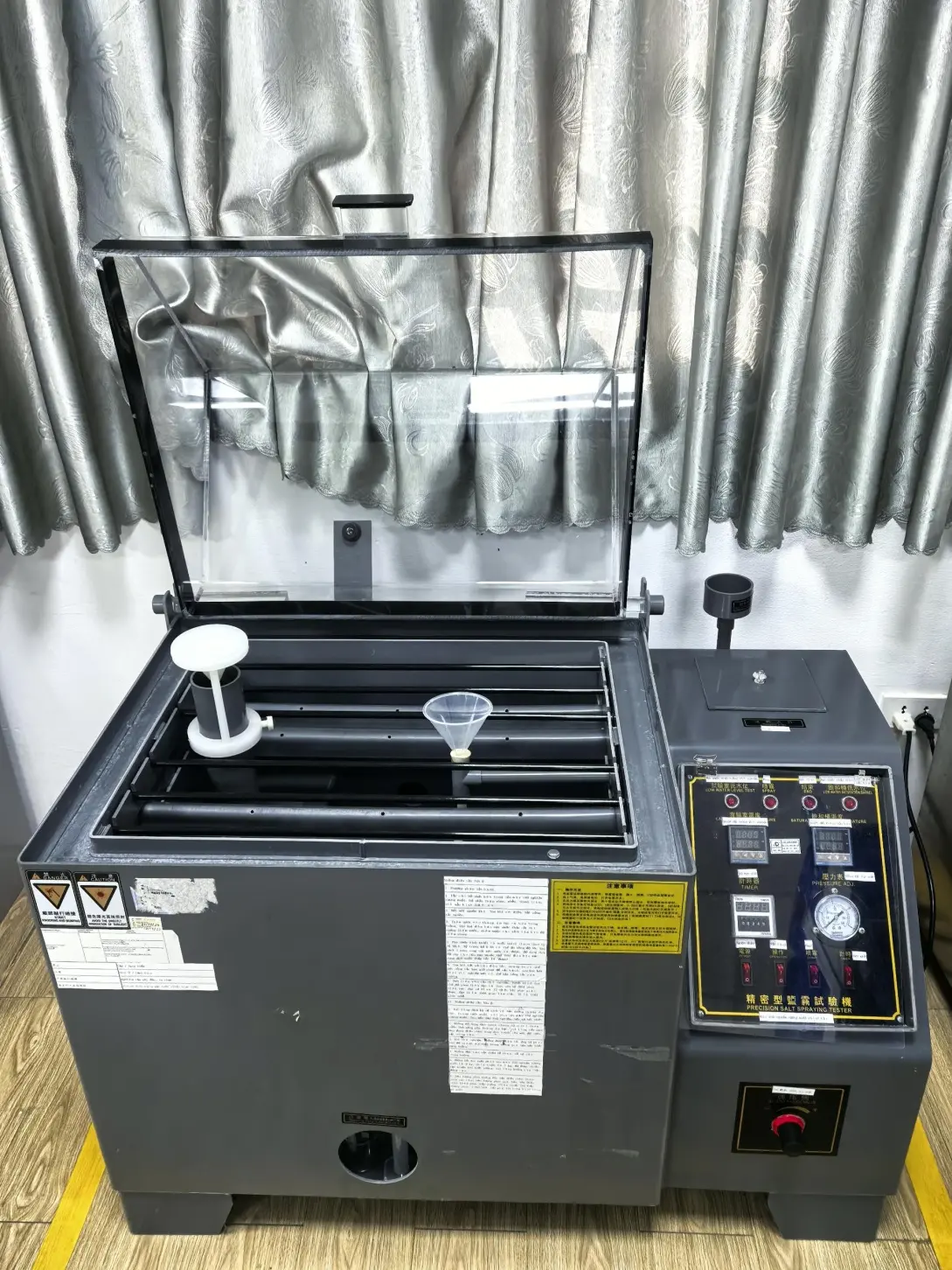

Salt spray testers are primarily used to simulate the corrosive effects of salty moisture on products in harsh marine or other environments, evaluating their corrosion resistance.
The following are common testing methods and procedures for salt spray testers: Neutral Salt Spray Test (NSS Test)
1. Test Preparation
● Equipment Inspection: Ensure all functions of the salt spray tester are normal, and that the spray system, temperature control system, and brine supply system are functioning correctly. Check that the brine tank, spray tower, collector, and other components are clean and free of impurities.
● Sample Preparation: Clean and degrease the test sample as required to remove surface oil, dust, and other impurities, taking care to avoid damaging the sample surface. For samples with special requirements, appropriate packaging or securing may be necessary to ensure stability during the test.
● Preparation of Salt Solution: Prepare a 5% ± 1% (w/w) salt solution using chemically pure sodium chloride (NaCl) and distilled or deionized water. The pH value of the solution should be between 6.5 and 7.2, which can be measured and adjusted using a pH meter. 1. If the pH value does not meet the requirements, it can be adjusted using hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution.
2. Test Setup
● Temperature Setting: Set the temperature inside the salt spray chamber to 35℃±2℃. Precisely adjust the temperature using the equipment's temperature control system to maintain a stable test temperature.
● Spray Pressure Adjustment: Adjust the spray pressure to ensure uniform and stable spraying of the brine. Typically, the spray pressure is maintained within the range of 0.14 - 0.17 MPa, which can be adjusted using a pressure regulating valve and monitored using a pressure gauge.
● Spray Volume Adjustment: Place at least two collectors inside the salt spray chamber. The collectors should be positioned where they are not obstructed by the sample and are at least 100 mm from the chamber wall. Adjust the spray volume to an average of 1 - 2 mL/80 cm²·h. Measure and adjust the volume by measuring the volume of brine collected by the collectors over a certain period.
3. Test Execution
● Sample Placement: Place the prepared sample inside the salt spray chamber, maintaining an appropriate distance between samples to avoid mutual obstruction of the spray. Ensure that the sample surface can uniformly receive salt spray deposition. The sample placement angle is typically determined according to product standards or relevant regulations, generally between 15° and 30°, to simulate the angle at which salt spray corrosion might occur during actual use.
● Start-up Test: After confirming that all parameters are set correctly, start the salt spray tester and begin the spray test. During the test, the equipment operation should be observed regularly, including temperature, spray status, and brine level, to ensure stable test conditions. At the same time, avoid frequently opening the salt spray chamber door to prevent affecting the test environment.
4. Test Cycle and Inspection
● Test Cycle: The test cycle is determined based on the product's usage environment, expected lifespan, and relevant standards. It generally ranges from a few hours to several days or even months. For example, a preliminary assessment of the corrosion resistance of some common metal products may require a 24-48 hour test; while products exposed to harsh marine environments for extended periods may require hundreds of hours of testing.
● Intermediate Inspection: During the test, apart from regularly observing the equipment operation, excessive human intervention should generally be avoided when inspecting the samples. However, in certain specific situations, such as when the test cycle is long, the samples can be visually inspected at specified time intervals to observe for signs of corrosion, such as rust, discoloration, and peeling, and these signs should be recorded. Care should be taken during inspection to avoid disrupting the salt spray coverage on the sample surface.
5. Test Completion and Result Evaluation
● Test Completion: After the predetermined test cycle is reached, stop the salt spray tester and remove the samples.
● Sample Cleaning: Gently rinse the sample surface with running water to remove salt spray deposits, then rinse with distilled or deionized water to remove residual salt. After cleaning, the samples can be air-dried at room temperature or dried at low temperature using a hairdryer or similar equipment.
● Result Evaluation: Evaluate the tested samples according to product standards or relevant specifications. Common evaluation methods include visual inspection, observing the degree of corrosion on the sample surface, such as the number, size, and distribution of corrosion spots, and the proportion of corrosion area; gravimetric method, assessing corrosion loss by the change in sample weight before and after the test; and metallographic analysis, observing changes in the internal structure of the sample due to corrosion. Different products and application scenarios may employ different evaluation indicators and methods.
Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (ASS Test)
1. Test Preparation
● Equipment and Sample Preparation: Similar to the neutral salt spray test, ensure the salt spray testing equipment is functioning properly and pre-treat the samples.
● Preparation of Salt Solution: Add an appropriate amount of glacial acetic acid (CH₃COOH) to a prepared 5%±1% sodium chloride solution to adjust the pH value to between 3.1 and 3.3. Use chemically pure reagents and distilled or deionized water for preparation, and accurately measure and adjust the pH value using a pH meter.
2. Test Setup and Execution
● Test Setup: Set the temperature to 35℃±2℃. Spray pressure, spray volume, and other parameters are set the same as in the neutral salt spray test.
● Test Procedure: Place the sample in the salt spray chamber and start the test according to the set conditions. Observation and maintenance requirements during the test are the same as in the neutral salt spray test.
3. Test Cycle, End, and Result Evaluation
● Test Cycle: Usually shorter than the neutral salt spray test cycle, determined according to product characteristics and standards, generally between 16 and 96 hours.
● Test End and Cleaning: After the test cycle is completed, stop the test, remove the samples, and clean them using the same method as for the neutral salt spray test.
● Result Evaluation: The evaluation method is similar to the neutral salt spray test. However, because the acetic acid salt spray test is more corrosive, the degree of corrosion of the samples may be more severe within the same test cycle. Evaluation should be based on the corresponding more stringent standards to determine the product's corrosion resistance.
Copper Accelerated Acetic Acid Salt Spray Test (CASS Test)
1. Test Preparation
● Equipment and Sample Preparation: Inspect and clean the salt spray tester to ensure normal operation, and pre-treat the samples.
● Preparation of Salt Solution: Add copper chloride (CuCl₂·2H₂O) to a 5%±1% sodium chloride solution, with a concentration of 0.26g/L±0.02g/L. Then add glacial acetic acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 3.1-3.3. Ensure reagent purity and use suitable water for preparation, and accurately measure and adjust the pH value.
2. Test Setup and Execution
● Test Setup: Set the temperature to 50℃±2℃. The spray pressure, spray volume, and other parameters are set the same as for the neutral salt spray test.
● Test Procedure: Place the sample in the salt spray chamber and start the test according to the set conditions. Due to the high test temperature, closely monitor the equipment operation during the test to prevent malfunctions from affecting the test results.
3. Test Cycle, End, and Result Evaluation
● Test Cycle: Generally short, possibly between 8-48 hours, depending on the product standard.
● Test End and Cleaning: Stop the test after the test cycle is reached, remove the sample, and clean it using the same method as before.
● Result Evaluation: Due to the extremely corrosive nature of this test, the corrosive effect on the samples is rapid and significant. Evaluation is based on standards specifically developed for the CASS test, assessing the product's corrosion resistance by evaluating aspects such as the sample's external corrosion characteristics and corrosion rate, in order to determine the product's protective capability in harsher corrosive environments.
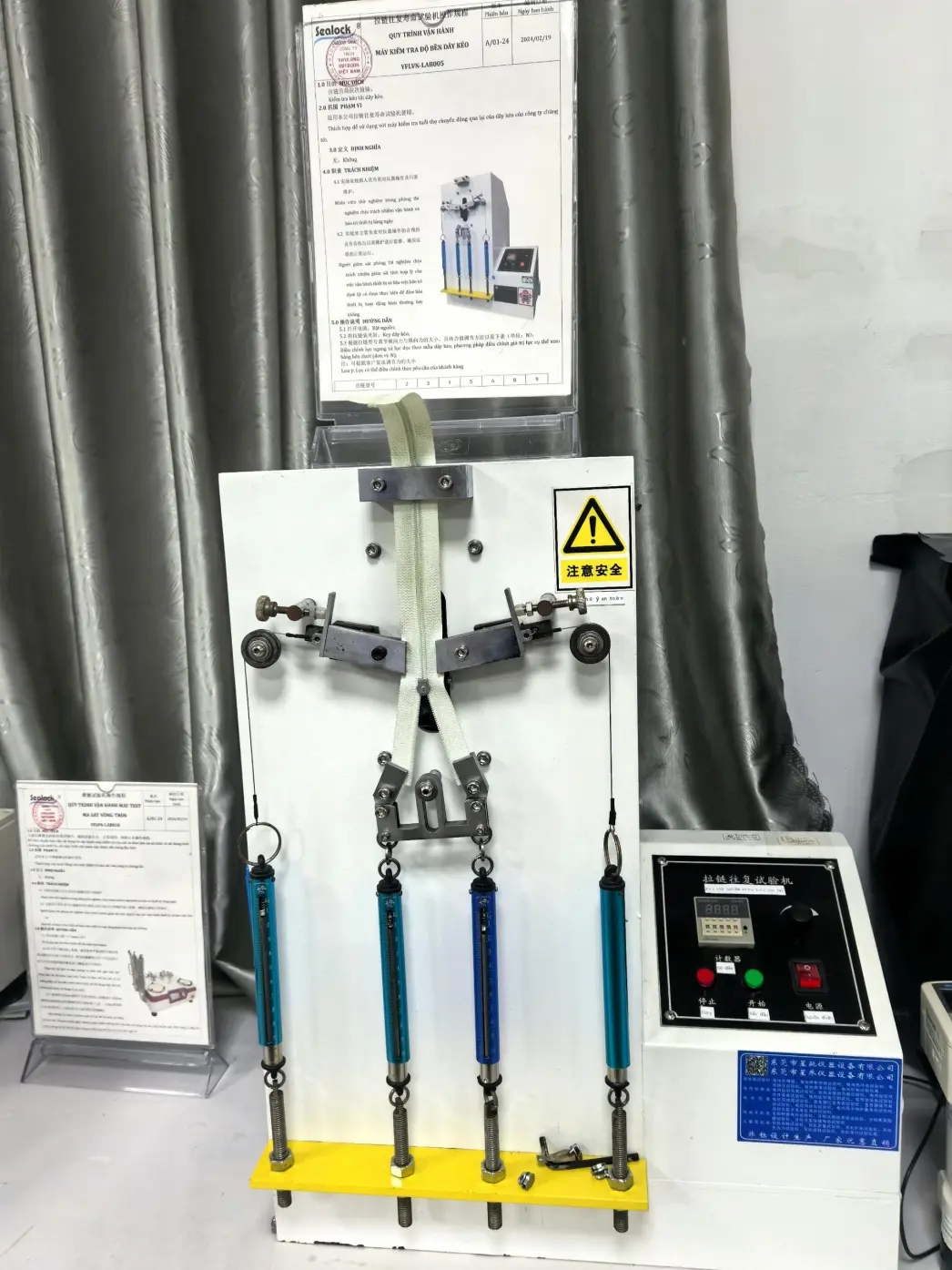
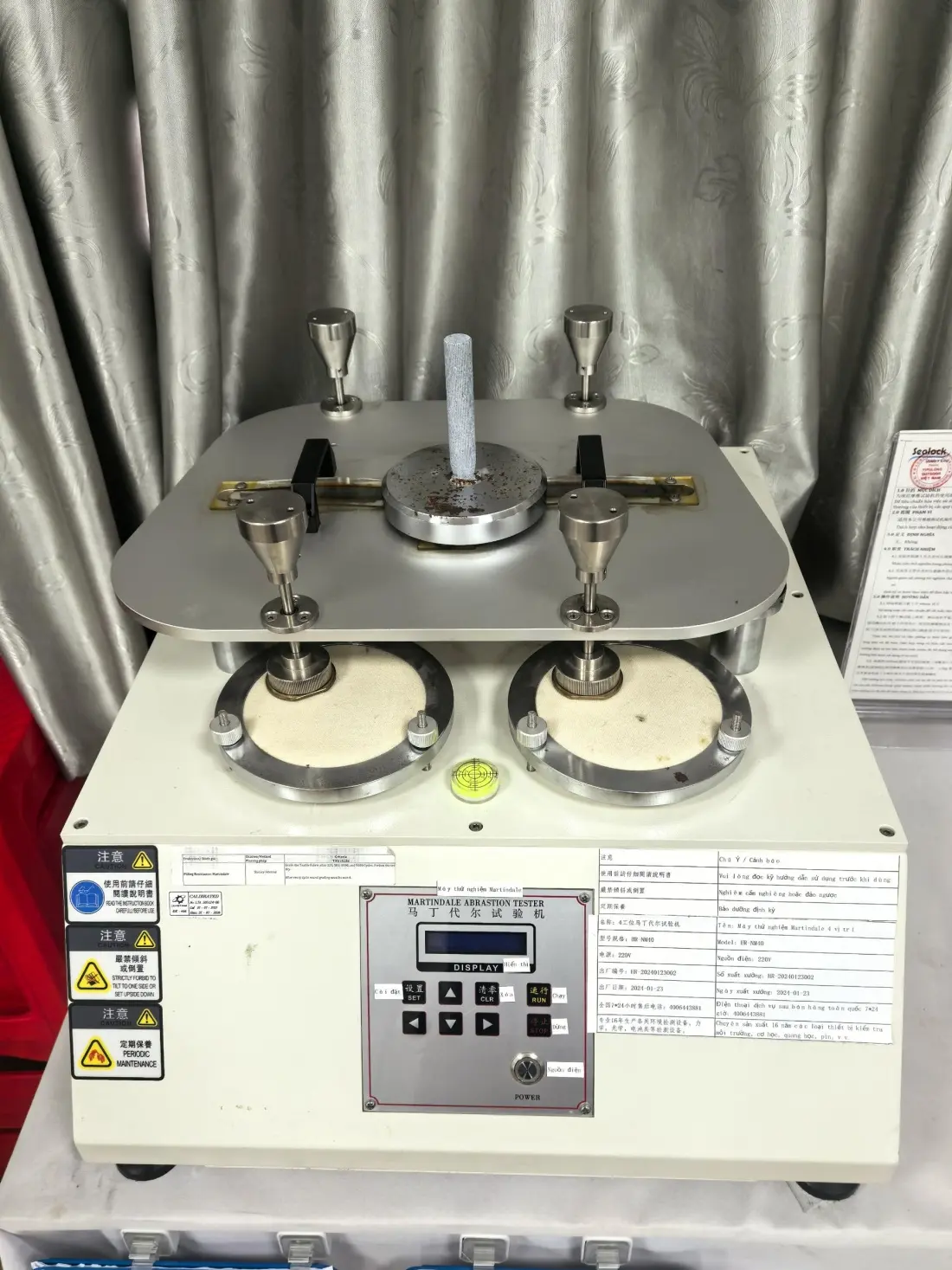
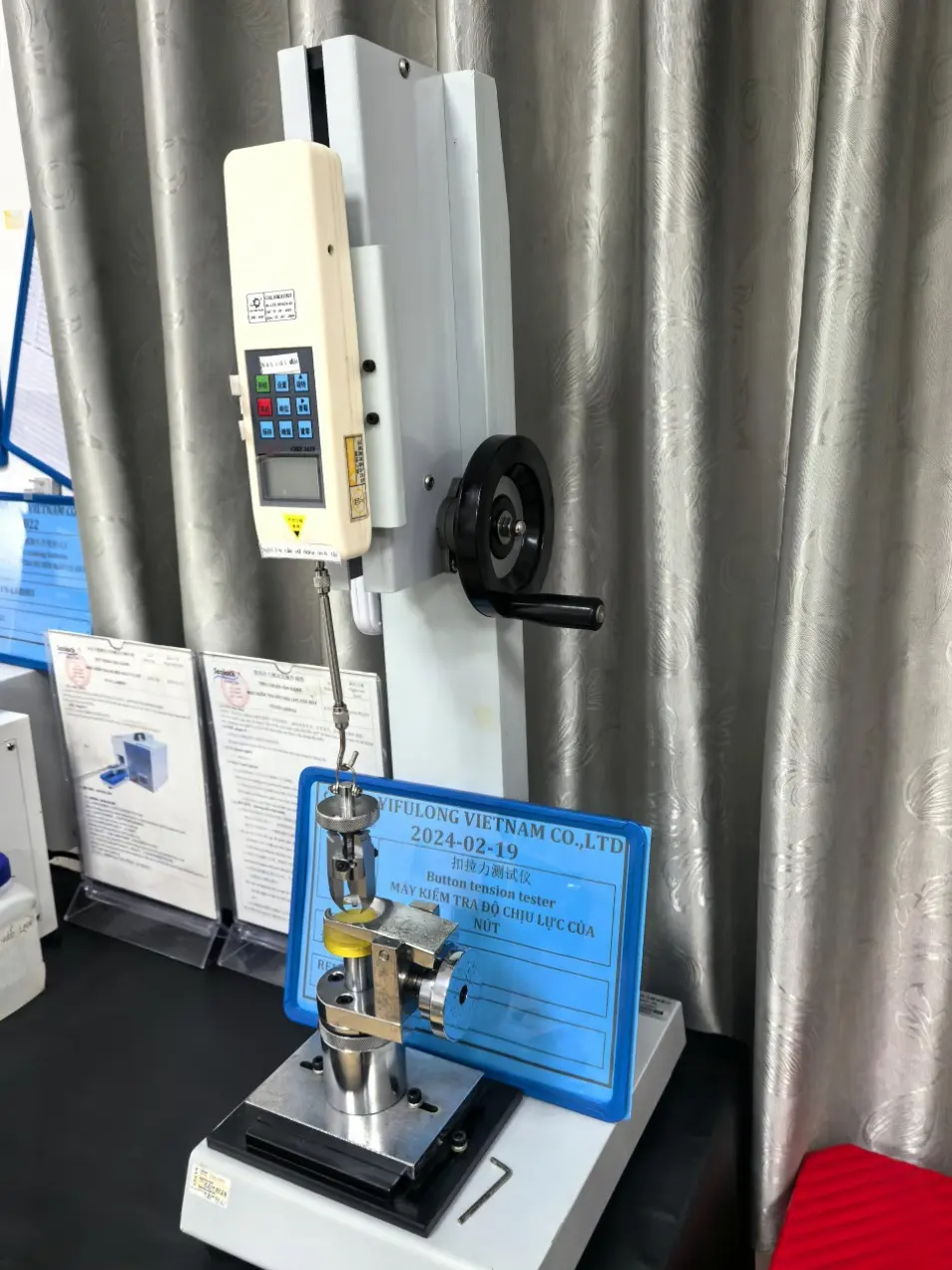
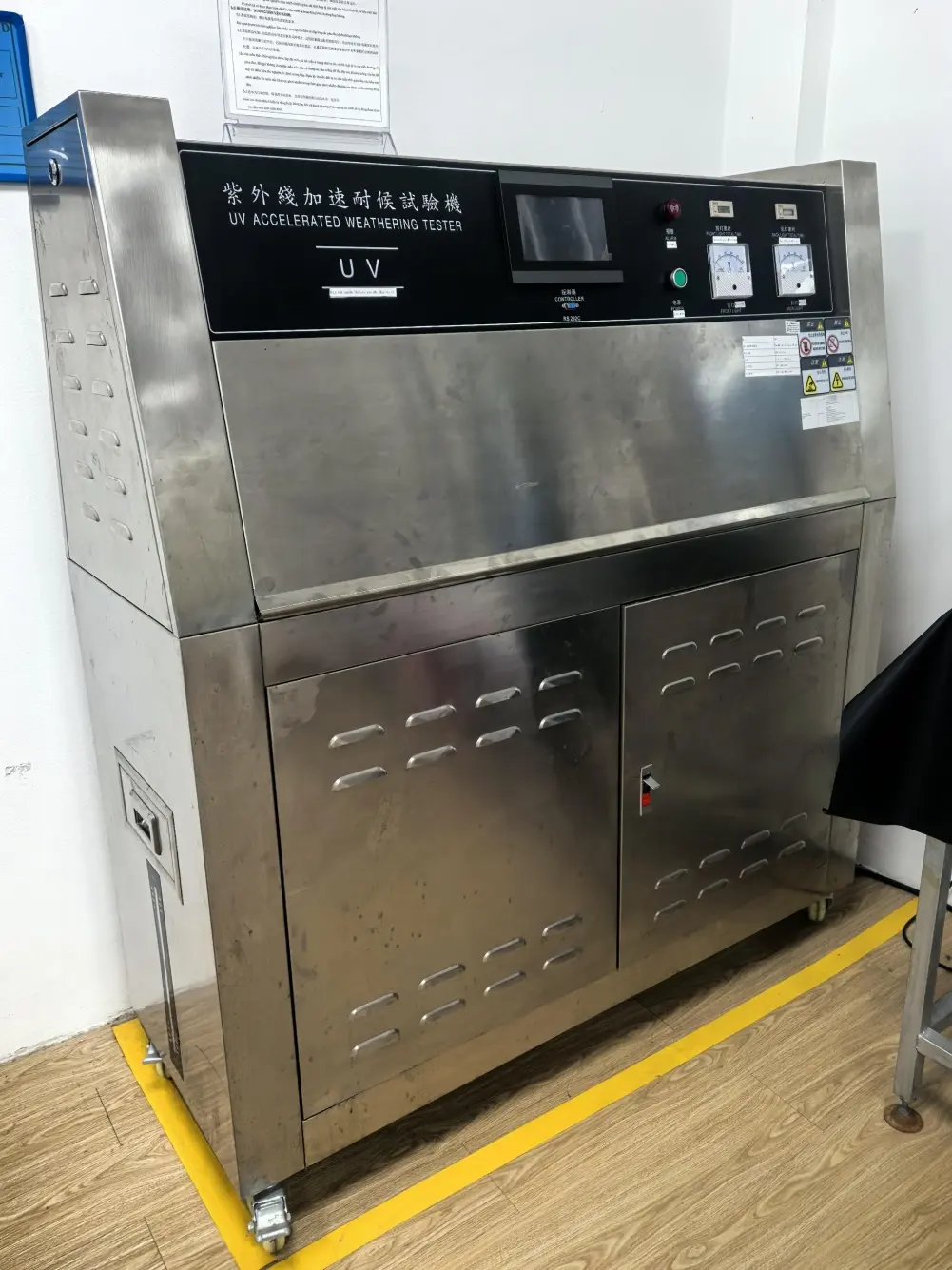
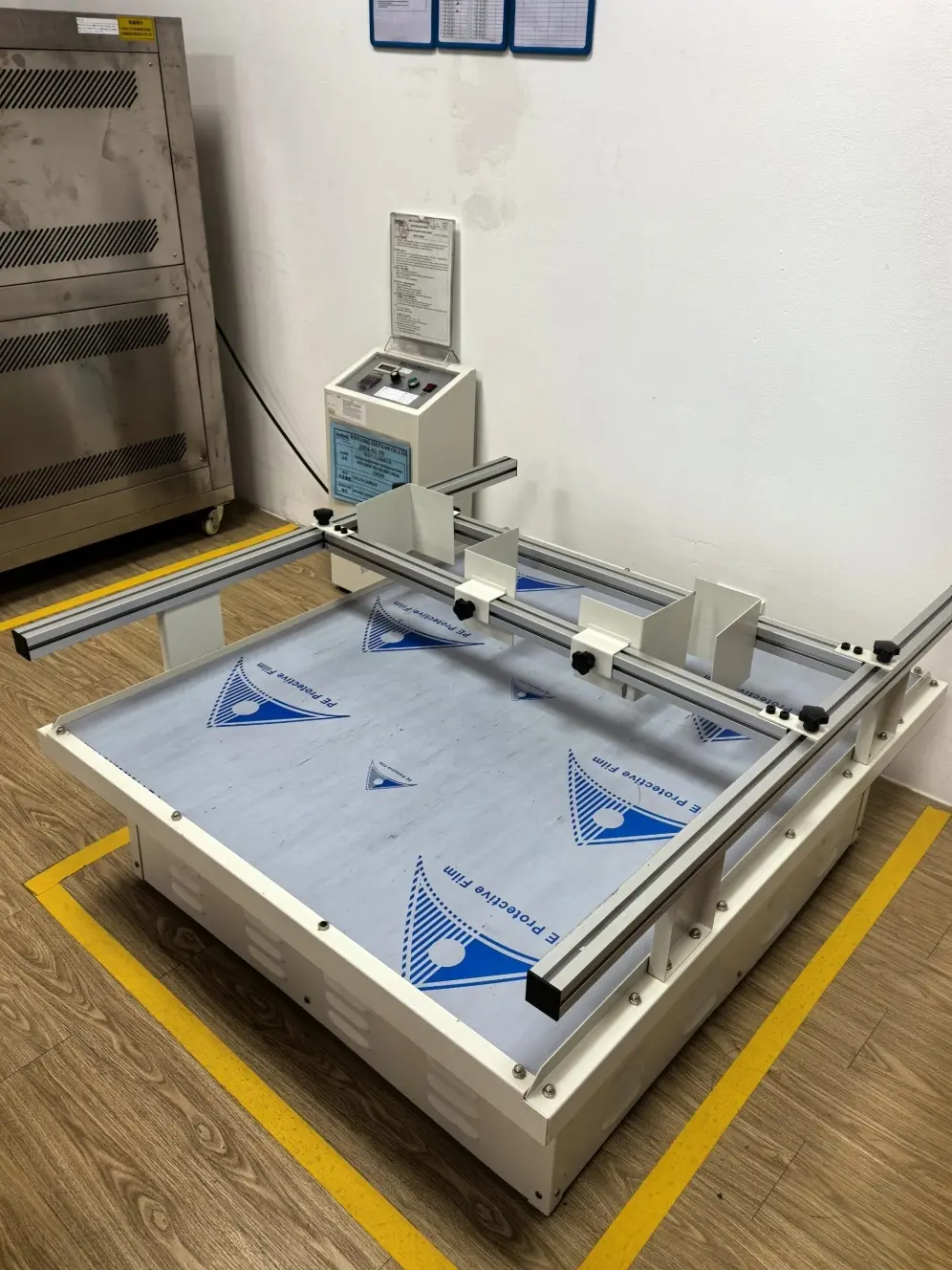
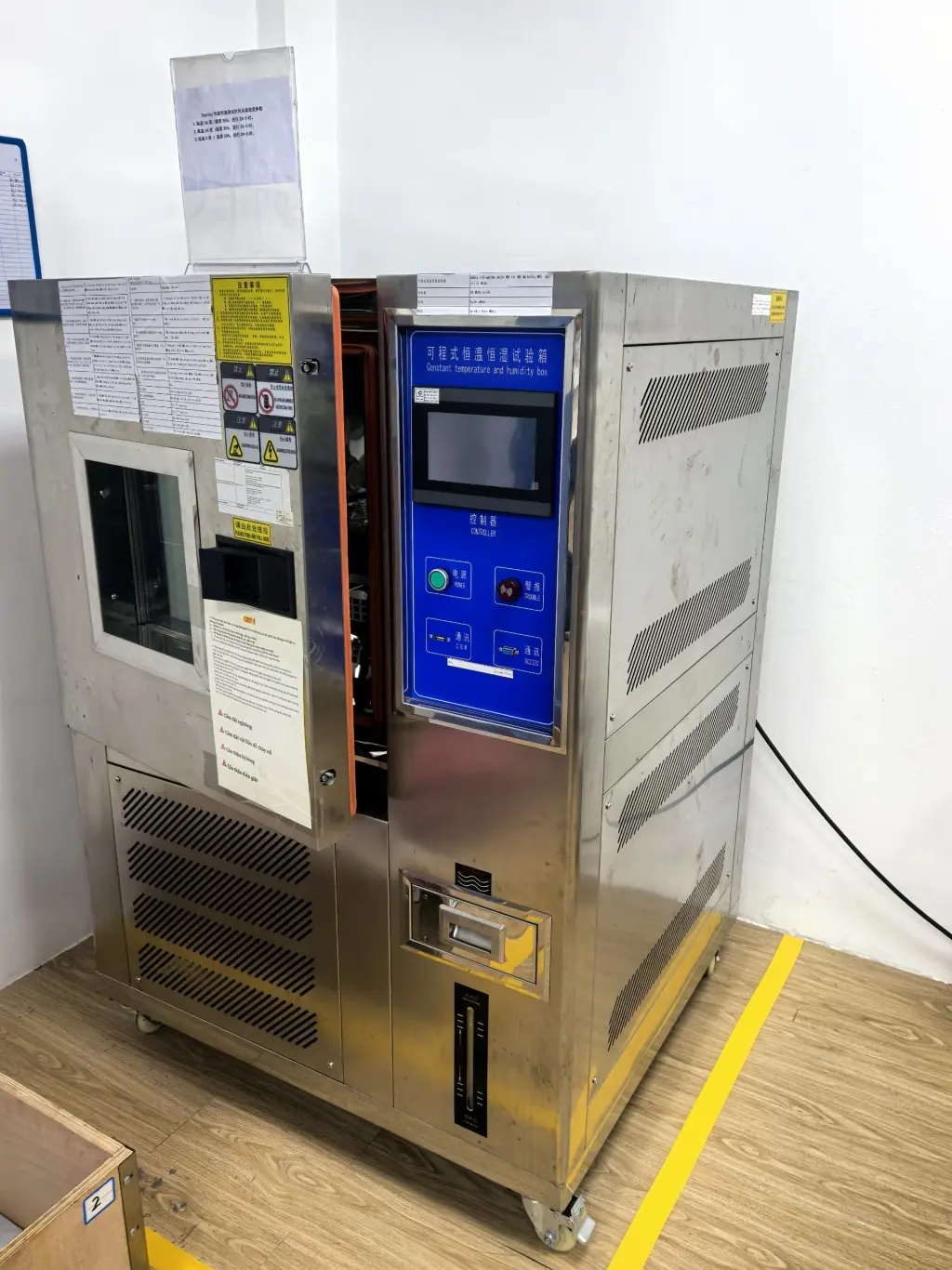
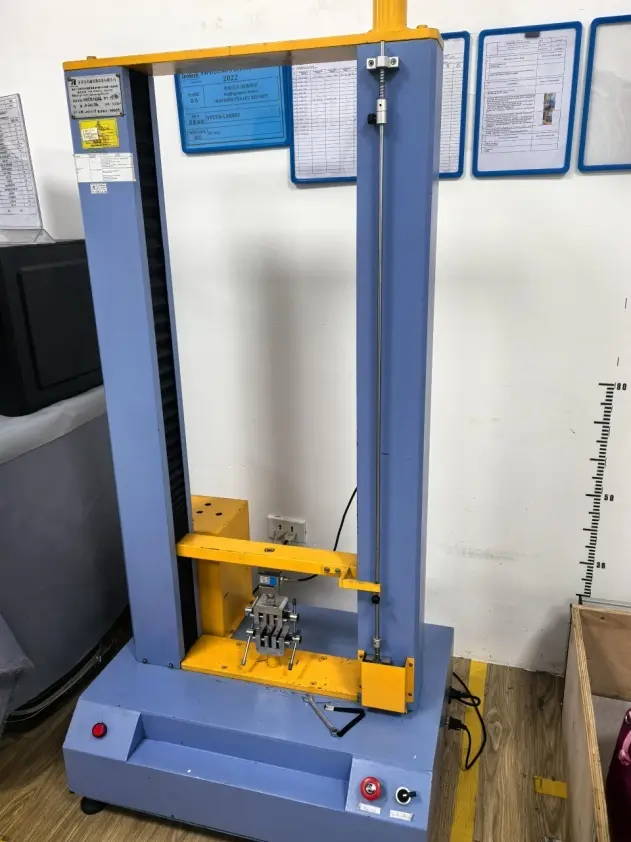
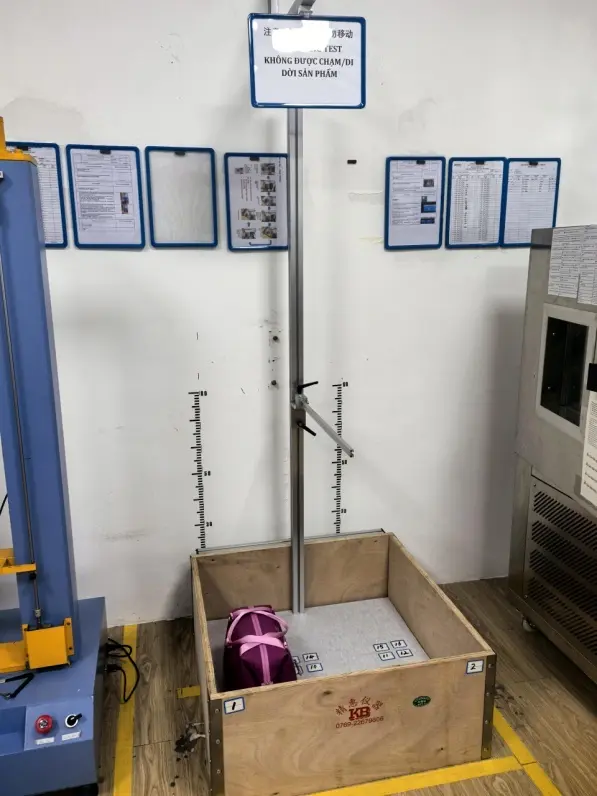





















Dongguan Machinery












Vietnamese Machines